Digoxin
Uses
- AF and atrial flutter
- Heart failure
Chemical
Sugar-Steroid-Lactone
Presentation
Main Actions
- Cardiac slowing and recuced rate of conduction throught the AV node
- Increased contractility
- Rhythm disturbances (heart block or increase ectopic pacemaker activity)
Mode of action
Indirect
Digoxin has a central effect which results in increased vagal activity. The increase in AV conductin is manifested as an increase on PR interval.
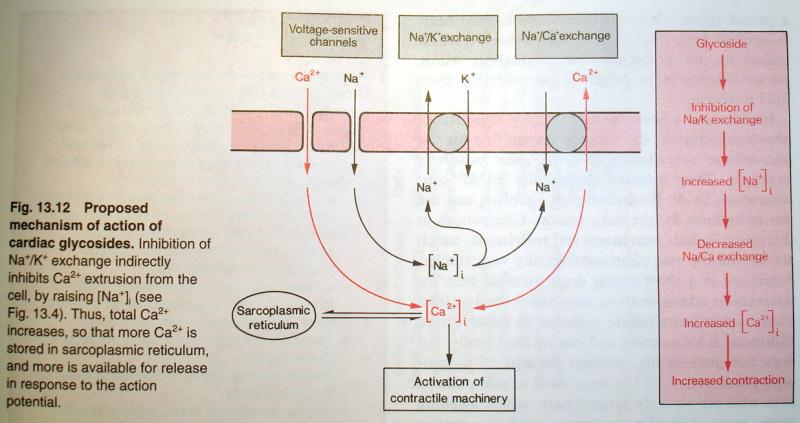
Direct
Digoxin blocks the Na/K ATP-ase, competitively binding to the K+ binding site. This has several effects:
- A rise in [Na]i and decrease in K+ which results in a slowing of AV conduction (Potassium efflux essential for repolarisation).
- Increased [Na]i slows extrusion of Ca2+ which depends on a Na/Ca antiporter
- Increased [Ca2+]i results in an increase in SR calcium content and increased release during an action potential. This increases contractility.
Route of administration / Dose
10-20µg/kg 6 hourly enterally or parenterally until desired effect achieved. Must be given slowly, if parenterally (25 µg/min). Peak effects 2 hours after administration.
Effects
- Increased force of contraction
- Heart rate slows - depression of SA node discharge, AV conduction, AV node refractry period and indirect vagotonic activity.
Toxicity / Side effects
Frequent. Anorexia, nasuea, vomiting, diarrhoea and abdo pain. Arrythmias. Exacerbated by hypokalaemia, hypernatraemia, hypercalcaemia, hypomagnesaemia, acid-base disturbance, hypoxaemia and renal failure.
Kinetics
Absorption
Highly variable GI absorption with bioavailability of 60-90%.
Distribution
20-30% protein bound in the plasma, but has a VD = 5-11 l/kg. Concentrationin cardiac tissues 15-30 times that in plasma.
Metabolism
Less than 105 undergoes hepatic metabolism
Excretion
50-70% o administered dose excreted unchanged in the urine. Elim T&fract12;=1.6 days