Suxamethonium
Uses
- Wherever rapid and profiund neuromuscular blockade is required
- To modify fits after ECT
Chemical
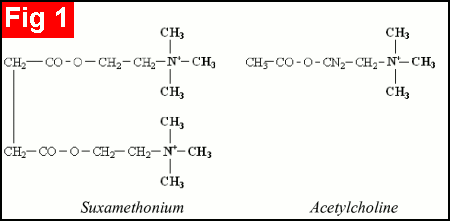
The dicoline ester of succinic acid
Preentation
As a clear acqeuos solution containing 50mg/ml of suxamethonium chloride which should be stored at 4°C
Main Action
Brief neuromuscular blockade in skeletal muscle
Mode of action
Prolonged depolarisation of skeletal muscle fibres to a membrane potential above which an action potential can be triggered.
Route of administration / Dose
iv 0.5 - 2mg/kg. Onset of action within 30s and duration 3-5 mins. Infuion of a 0.1% solution at 2-15mg/kg/hr will result in a 90% twitch depression. The im dose is 2.5mg/kg. Equal doses on a mg/kg basis havea shorter duration in infants.
Effects
CVS - bradycardia and a small increase in blood pressure ion repeated doses.
RS - Apnoea due to skeletal muscel paralysis
CNS - Initially causes fasiculations and then a phase 1 deploarising block. The characteristics of this during partial paralysis are:
- Well sustained tetanus during stimulation at 50-100Hz
- No post-tetanic facilitation
- Train-of-four ration > 0.7
- Potentiation by anticholinesterases
With repeated administration (or a large total dose) a phase 2 block may develop. The characteristics during partial paralysis are:
- Poorly sustained tetanus
- Post-tetanic fasciculation
- Train-of-four ratio < 0.4
- Reversal by anti-cholinesterases
- Tachyphylaxis
Intracranial and intraocular pressure are both raised following the administration of suxamethonium.
AS - Intragastric pressure increases by 7-12 cmH2O while the lower oesophagealspincter tone decreases. Salivation and gastric secretion are increased.
Metabolic/Other - Serum potassium concentration increases by 0.2 - 0.4 mmol/l